Technology
Data Ethics and Bias - Building Fair Technology for Everyone
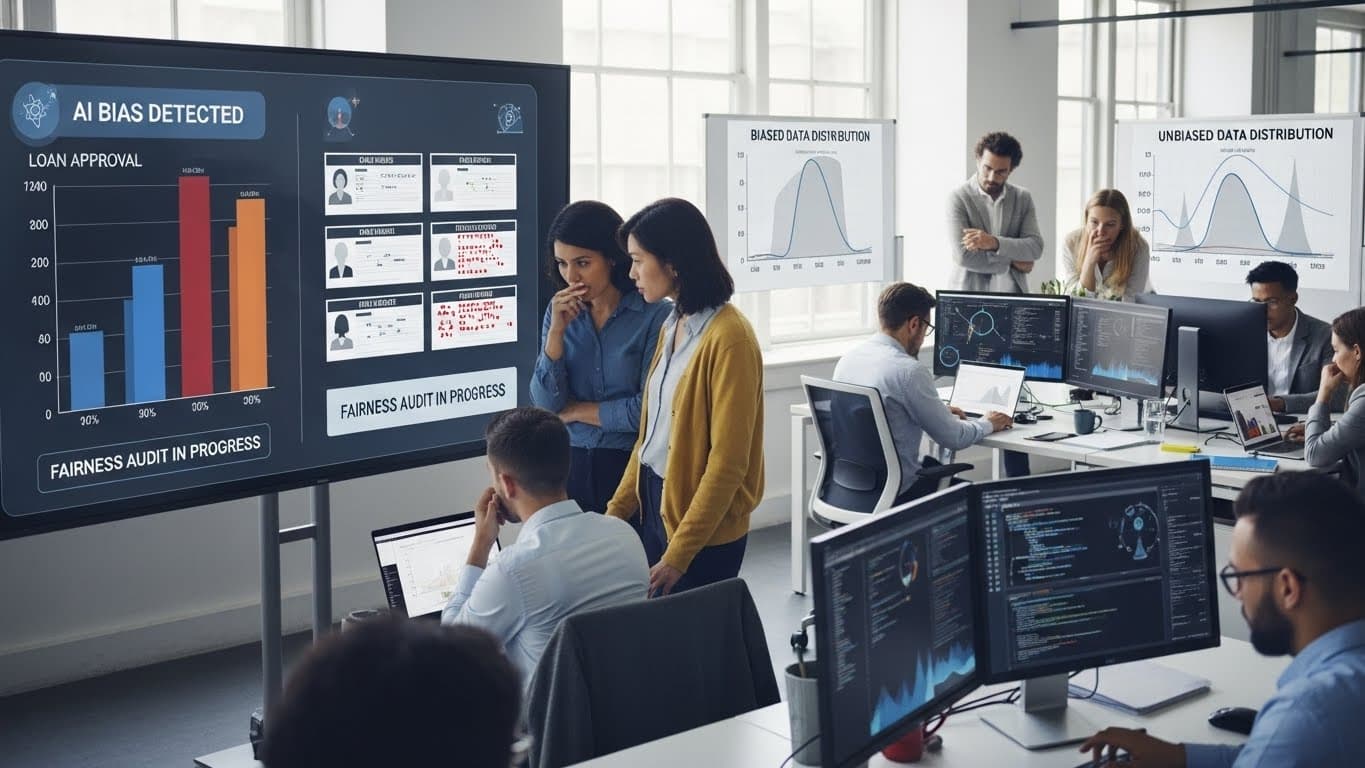

In our data-driven world, where every click, purchase, and search feeds massive algorithms, data ethics have become more important than ever. Data ethics is about making sure the information we collect, analyze, and use respects people's rights, privacy, and fairness. At the heart of this conversation, there is bias, unfair preferences, or prejudices that sneak into data systems, often without anyone noticing. These biases can lead to real harm, like denying someone a job ora loan because of their race, gender, or background. Understanding data ethics helps us create technology that benefits everyone equally, not just a select few. This blog breaks it down simply, so anyone from students to business leaders can grasp why it matters and how to address it.
Data bias starts with the information we feed into systems. Most data reflect the real world, which isn't always fair. For example, if a hiring AI is trained on resumes from mostly male engineers from certain universities, it might favor similar candidates and overlook talented women or people from diverse backgrounds. This is called historical bias, where past inequalities get baked into the future. Similarly, selection bias happens when data only captures part of the picture, like surveying only active social media users, missing quieter voices. The result? Algorithms that amplify problems instead of solving them, affecting everything from credit scores to criminal justice predictions.
Privacy is another cornerstone of data ethics. Companies collect mountains of personal details, your location, shopping habits, and health records, often without clear permission. Ethical data use means getting informed consent, anonymizing information, removing names and identifiers, and giving people control over their data. Think of Europe's GDPR laws or California's privacy rules, they force companies to be transparent about data collection. Without these safeguards, breaches can expose sensitive info, leading to identity theft or discrimination. Ethical organizations prioritize privacy by design, building systems that protect data from the start.

Real-world examples highlight the stakes. Amazon's hiring tool was scrapped in 2018 after it discriminated against women, trained on male-dominated resumes. Facial recognition systems have misidentified people of color at higher rates, leading to wrongful arrests. On the positive side, healthcare AI trained ethically can spot diseases equally across populations, saving lives fairly. Governments and organizations are responding with regulations like the AI Act in Europe, mandating bias checks for high-risk systems.
Looking ahead, data ethics must evolve with technology. As AI gets smarter with generative models and big data, we need global standards, education in schools, and ethical AI certifications. Individuals can help by demanding transparency from apps, supporting diverse tech teams, and learning basic data literacy. Ultimately, ethical data practices ensure technology lifts everyone up, creating a fairer society.
In summary, data ethics and bias aren't abstract tech jargon, they're about building systems that respect humanity. By prioritizing fairness, privacy, and accountability, we turn potential pitfalls into opportunities for good. Whether you're using AI daily or shaping it, committing to ethics makes technology work for all.
Test Your Knowledge!
Click the button below to generate an AI-powered quiz based on this article.
Did you enjoy this article?
Show your appreciation by giving it a like!
Conversation (0)
Cite This Article
Generating...
.png&w=3840&q=75)